How to Automate Purchase Order Matching in Accounts Payable
Manual purchase order matching is one of the biggest bottlenecks in accounts payable departments. Finance teams waste hours cross-checking invoices with purchase orders, resolving mismatches, and tracking missing data. The result? Delayed payments, strained vendor relationships, and increased risk of costly errors.
Download your free eBook. Your AP Automation Wake-Up Call.
Calculating the Cost of Doing Nothing [2025 Edition].
The problem gets worse when organizations scale. More suppliers mean more invoices. More invoices mean more matching. More matching means more manual work.
This chain of events continues until finance teams drown in paperwork and strategic priorities are relegated to the backseat.
Automation is the way out. This post looks at how intelligent systems can transform your purchase order matching process, reduce costs, and free your team for higher-value work.
Table of Contents
- What is purchase order matching?
- Purchase order matching challenges
- The cost of manual PO matching
- How purchase order matching automation works
- Types of purchase order matching automation
- How to handle non-PO invoices
- Implementation best practices
- Measuring success
- Implementation challenges
- Future of purchase order matching
- Purchase order matching FAQs
- Ready to fix your AP bottlenecks?
What is purchase order matching?
Purchase order matching is the process of comparing invoices against purchase orders to confirm accuracy before payment. This verification ensures that your organization only pays for goods and services ordered and received.
The process typically involves several types of matching…
Two-way matching
2-way matching compares invoices to purchase orders, checking quantities, prices, and terms. This basic verification catches many common errors but misses situations where goods were ordered but never delivered.
Three-way matching
3-way matching adds a receiving report to the comparison, creating a more comprehensive verification. Three-way matching compares three key documents – purchase order, receiving report, and invoice – to ensure the goods or services ordered match what was received and invoiced.
Four-way matching
4-way matching extends the process by including inspection reports to verify the quality of received goods against the PO and receipt before payment is approved.
Each level of matching provides additional security but also increases complexity. Manual matching becomes much harder as organizations implement more thorough verification processes.
Purchase order matching challenges
Finance teams face endless obstacles when handling PO matching manually. Understanding these challenges helps explain why automation is now essential for modern accounts payable operations.
Document discrepancies
Invoices rarely match purchase orders perfectly. Suppliers use different formats, include varying levels of detail, and sometimes reference different product codes.
For instance, a purchase order might list “Widget A” while the invoice shows “Model WA-2025.” These naming variations force manual intervention to determine whether items match.
Price discrepancies create more complications…
- Suppliers applying different tax rates
- Additional shipping charges not included in the original purchase order
- Implementing price changes between order and delivery
Each variation needs human review to establish whether the difference is legitimate.
Missing information
Purchase orders are often incomplete, lacking information needed for matching…
- Partial deliveries splitting single orders into multiple invoices
- Service agreements spanning multiple billing periods
- Emergency purchases bypassing normal procurement processes, creating invoices without corresponding purchase orders
Receiving reports brings its own challenges…
- Warehouse teams recording deliveries differently than finance teams expect
- Damaged goods creating partial receipts
- Service deliveries leaving no physical trail for verification
Volume and timing demands
High-volume organizations process thousands of invoices monthly. Each invoice needs careful review against purchase orders and receiving reports. The manual effort scales linearly with invoice volume, creating bottlenecks during peak periods.
Early payment discounts add time pressure to the process. Suppliers offer 2% discounts for payments within 10 days. But manual matching is time consuming and it’s a hard ask to catch that discount. Accounts payable teams must choose between thorough verification and cost savings.
System limitations
Legacy ERP systems often lack refined matching capabilities. They might flag obvious discrepancies but miss subtle issues that ask for human judgment. Integration challenges hinder seamless data flow between procurement, receiving, and accounts payable systems.
Multiple systems create data silos. Purchase orders live in procurement software. Receiving reports exist in warehouse management systems. Invoices arrive through various channels.
Manual processes bridge these gaps, but at considerable cost.
The cost of manual PO matching
Manual purchase order matching inflicts direct and indirect costs that nibble away at profitability and operational efficiency. These costs go beyond obvious labor expenses to include opportunity costs, error-related expenses, and strategic limitations.
Processing costs
Each manual matching operation eats up time and resources. Finance teams spend hours comparing documents, researching discrepancies, and coordinating with suppliers and internal teams. That’s time better spent on strategic analysis, process improvement, or relationship building.
The matching process becomes even more expensive as organizations grow. Adding suppliers, product lines, or locations increases the manual effort required. And with growth, the linear scaling of manual processes becomes unsustainable.
Error-related costs
Manual processes introduce the risk of human error that produce downstream costs.
- Incorrect payments need reversal and reprocessing
- Duplicate payments demand recovery efforts
- Missed discrepancies lead to overpayments that might never be found
Fraud costs businesses 5% of their annual revenue every year. Manual matching processes provide insufficient protection against sophisticated fraud schemes. Fake invoices, inflated quantities, and unauthorized purchases slip under the radar with manual reviews.
Opportunity losses
Manual matching delays payment processing, preventing capture of early payment discounts. A typical 2/10 net 30 discount saves 2% of invoice value for payments within 10 days. Manual processing often prevents organizations from meeting these deadlines.
Supplier relationships suffer when payments are delayed because of PO matching bottlenecks. Late payments damage trust and can result in reduced credit terms or higher prices. Some suppliers impose late payment penalties that add direct costs.
Strategic limitations
Manual matching provides limited visibility into spending patterns and vendor performance. Data locked up in paper processes is unable to inform strategic decisions. Finance teams can’t analyze spending trends, identify cost-saving opportunities, or optimize vendor relationships.
The matching process cramps business growth. New suppliers, product lines, or locations require increases in manual effort. This scaling limitation forces organizations to choose between growth and operational efficiency.
How purchase order matching automation works
Automated purchase order matching solutions use AI and machine learning to perform the comparisons that finance teams traditionally handle manually. These systems process structured and unstructured data to identify matches, flag discrepancies, and route exceptions for human review.
Intelligent document processing
Modern automation platforms use artificial intelligence to read and understand invoices, purchase orders, receipts, and more. Unlike traditional template-based systems, AI document processing platforms reduce the configuration needed for different document formats. Though initial setup and training data are still required for the best performance.
The technology combines optical character recognition – OCR – with natural language processing to extract relevant data fields. Machine learning algorithms improve accuracy over time, learning from corrections and feedback to handle new document types automatically.
Rossum reports average accuracy rates of up to 96% using AI specifically trained on transactional documents. With an out-of-the-box extension that checks whether there’s a purchase order with a corresponding ID in your database. It also checks whether the line items on the invoice match the line items on the PO.
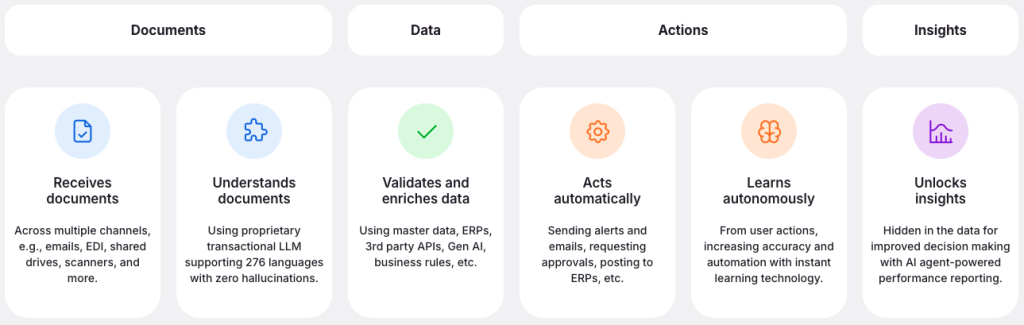
Document journey in Rossum – from ingestion to insights.
Automated PO matching logic
Matching algorithms compare extracted data across multiple documents. The system assesses quantities, prices, descriptions, and other fields to understand whether documents match within acceptable tolerance levels.
Advanced systems handle complex scenarios that challenge manual reviewers. They can…
- Match partial deliveries to original purchase orders
- Handle quantity variations within predetermined ranges
- Recognize legitimate price changes based on contract terms
Exception management
Not every invoice matches perfectly with its corresponding purchase order. Automation systems flag these discrepancies for human review while providing context and recommendations for resolution. This structured approach to exception handling improves efficiency and reduces errors.
Some exceptions are super complicated…
- A vendor invoices for the full amount but only part of the order was shipped
- The PO lists ten SKUs but the invoice merges them into three bundled line items
- A service invoice includes time-based charges and one-off expenses
- A price includes a rush fee not noted on the original PO
- An item arrives damaged, but the invoice still reflects the full cost
These are the frequent mismatches that slow everything down. Automation can flag them and route to the right team, but someone still needs to decide what’s acceptable. The goal is to reduce this confusion so your AP team can focus on decisions, not be forced to play at being detectives.
Exception workflows route specific types of discrepancies to appropriate team members. Price variances might go to procurement teams. Quantity discrepancies could route to receiving departments. This targeted routing accelerates resolution.
Intelligent document processing solutions like Rossum provide contextual recommendations for resolving discrepancies, reducing the time finance teams spend on manual reviews.
Integration capabilities
Modern automation platforms integrate with existing ERP systems, procurement software, and financial management tools. This integration eliminates manual data entry and ensures consistency across systems.
Real-time data synchronization ensures all systems are updated as invoices move through the matching process. Approved payments flow automatically to payment systems. Rejected invoices return to suppliers with detailed explanations.
Types of purchase order matching automation
Organizations can implement different levels of automation based on their needs, risk tolerance, and existing infrastructure. Each approach offers distinct advantages and implementation considerations.
Rule-based automation
Rule-based systems use predetermined criteria to match invoices with purchase orders. These systems handle straightforward matches automatically while flagging exceptions for manual review. Rules might include exact quantity matches, price tolerance ranges, or specific vendor requirements.
This approach works well for businesses with standardized processes and predictable invoice formats. Implementation is relatively uncomplicated, and the logic is transparent to users. However, rule-based systems need ongoing maintenance as specifications change.
AI-powered automation
AI systems analyze patterns in historical matching data to make increasingly accurate decisions. But they still need human oversight for complex exception cases. These systems handle complex scenarios that would require manual intervention in rule-based systems. AI can recognize patterns, adapt to new situations, and improve accuracy over time.
Machine learning algorithms analyze successful matches and exception resolutions to refine their decision making. This continuous improvement reduces the percentage of invoices requiring human review and increases matching accuracy.
Rossum’s advanced AI – Rossum Aurora – for example, was trained on millions of transactional documents to recognize patterns and handle complex matching scenarios automatically.
Rossum Aurora – Tailor-made for your transactional documents.
Hybrid approaches
Many organizations combine rule-based and AI-powered automation to optimize performance. Rules handle clear-cut scenarios while AI addresses complex cases. This hybrid approach provides the reliability of rule-based systems with the flexibility of artificial intelligence.
Hybrid systems allow organizations to maintain control over high-risk business transactions while automating routine processing. They can implement strict rules for high-value purchases while allowing AI to handle standard invoice matching.
How to handle non-PO invoices
Not all invoices follow the PO process – think utility bills, legal retainers, marketing spend, rent… Documents that don’t follow a structured procurement process.
Non-PO invoices that need their own workflows involving coding, multi-level approvals, policy checks, and tracking.
Automation platforms tackle these by tagging invoice types, suggesting GL codes based on past entries, and routing invoices to the right budget owner for review. Department heads can approve directly, while finance tracks spend against budgets. Automating these exceptions reduces the pile-up that usually builds around month-end.
Implementation best practices
Successful PO matching process automation calls for painstaking planning, phased implementation, and ongoing optimization. These purchase order matching best practices will help you maximize returns while minimizing implementation risks.
Set realistic expectations for AI implementation
You can’t simply flip a switch and turn on PO matching. We’re not talking about installing a new piece of software.
Think of it as onboarding a new team member. It needs to understand how your company operates. Your business rules. Vendor naming patterns. Partial shipment rules vs single. Pricing strategy.
You’ll kick off with training the AI how to address your company’s quirks, correcting assumptions, and refining your workflows. As the AI processes more documents and receives feedback, accuracy will improve.
Plan for this learning curve and you’ll avoid disrupting daily operations and improve long-term results.
Data quality verification
Clean, consistent data is the foundation of effective automation. You must establish data quality standards for purchase orders, vendor information, and product catalogs before implementing automation.
Start with your Vendor Master File. Inconsistent naming conventions, duplicate records, or outdated contact details cause false exceptions that derail automation. Before you implement anything, take time to audit and clean up your supplier records. Align units of measure, standardize naming conventions, and remove inactive vendors. It’s not glamorous work, but it pays off every time the system avoids a false exception.
Process standardization
Automated systems work best with standardized processes. Start by documenting current matching procedures, identify variations, and establish standard workflows before implementing automation.
Exception handling procedures demand particular attention. Clear escalation paths, approval authority levels, and resolution timelines help ensure smooth automation deployment. These processes should account for different types of discrepancies and appropriate responses.
Phased implementation
Gradual rollout reduces implementation risk and allows for refinement based on real-world experience. For instance, you could start with a single vendor, product category, or business unit before opening to full deployment.
Each phase should include success metrics and evaluation criteria. Processing time, exception rates, and user satisfaction help measure automation effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Training and change management
Automation changes how finance teams work. So it’s important to introduce training programs to cover new processes, system usage, and exception handling procedures. Your team needs to understand how automation works and when manual intervention is required.
Change management extends beyond training to include communication, support, and continuous improvement. Regular feedback sessions help identify issues and opportunities for enhancement.
Let’s be brutally honest, when the subject of automation comes up, the first thing your AP team thinks is “will I lose my job?”
The reality is, automation doesn’t remove the need for human judgment, process knowledge, or cross-team coordination. It just shifts the focus.
Rather than spending hours tracking down a missing PO number, your team can spend time on vendor negotiations, compliance checks, or spend analysis.
Automation takes care of the repetitive, tedious part. The grunt work that burns people out. When positioned this way, automation transforms your team so it’s less about data entry, it’s about insight and control.
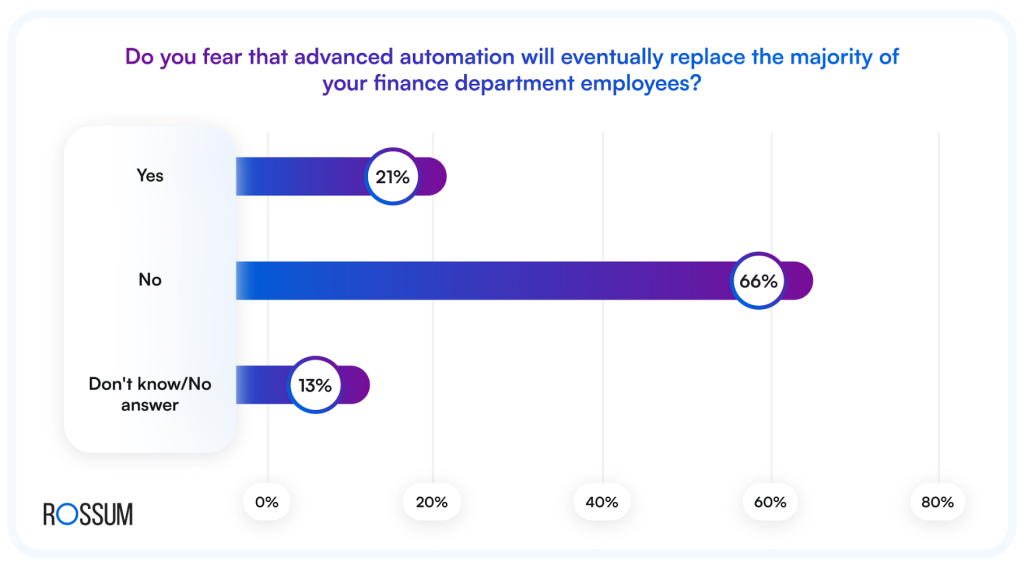
Our Document Automation Trends 2025 survey showed that 66% of finance leaders don’t fear losing their teams to advanced automation. Seeing it as a tool to augment rather than replace their workforce.
Measuring success
Effective measurement will help you understand automation impact and identify improvement opportunities. Key performance indicators must align with your business objectives and provide actionable insights.
Processing efficiency metrics
Processing time per invoice gives you a direct measure of automation impact. Automated AP solutions can cut invoice processing times by up to 80%. Exception handling time also decreases as systems provide better context and recommendations.
Throughput capacity measures how many invoices the system can process without additional resources. Automation dramatically increases processing capacity, allowing your organization to handle growth without having to increase headcount.
Accuracy improvements
Exception rates indicate how often invoices need manual intervention. 68% of businesses report invoice error rates of 5% or lower, with 25% reporting error rates of less than 1%.
Error rates measure incorrect payments, duplicate payments, and other processing mistakes. Automation typically reduces error rates by 80-90% compared to manual processes.
Financial impact
Cost per invoice processed shows the direct financial benefit of automation. According to Ardent Partners’ 2024 State of ePayables report, organizations using AP automation software reduce invoice processing costs by 80%. Cutting processing times from weeks to days. With the average cost of processing a single invoice manually reaching $15-$40, automation is essential for financial sustainability.
Early payment discount capture increases as faster processing enables your team to meet discount deadlines. This improvement directly impacts cash flow and vendor relationships.
Strategic benefits
Vendor relationship improvements come from faster, more accurate AP processing. Supplier satisfaction surveys and payment cycle times provide measurable indicators of relationship health.
Employee satisfaction often improves as automation eliminates boring, repetitive tasks and allows focus on strategic activities. Employee surveys and retention rates help measure this impact.
Implementation challenges
Businesses face multiple but predictable challenges when implementing purchase order matching automation. Understanding these obstacles will help your team prepare appropriate responses and mitigation strategies.
Data integration complexity
Connecting automation systems with existing ERP, procurement, and financial systems requires careful planning. Legacy systems often lack advanced integration capabilities, needing custom development or middleware solutions.
Data mapping between systems creates additional complexity. Field names, data formats, and business rules must align across platforms. This alignment calls for technical effort and business process analysis.
User adoption resistance
Your finance team might resist automation because of concerns about job security or accounts payable process changes. Clear communication about automation benefits and new role definitions help address these concerns.
Training programs must address both technical system usage and conceptual understanding of automated processes. Your team needs to understand when and how to intervene in automated workflows.
Vendor cooperation
Automation success depends partly on vendor cooperation with e-invoicing and data standardization. It’s likely that some suppliers will resist changes to their invoicing processes or lack technical capabilities for electronic submission.
Vendor onboarding programs help suppliers understand new requirements and provide necessary support. These programs should include technical assistance and clear timelines for compliance.
Ongoing maintenance
There will be ongoing maintenance and optimization of your automation systems. Business rule updates, system integrations, and performance monitoring demand dedicated resources.
Continuous improvement processes will help your organization refine automation rules and expand coverage. Regular reviews of exception patterns and user feedback will identify optimization opportunities.
Future of purchase order matching
The development of purchase order matching automation continues as technology advances and business requirements become more and more sophisticated. Understanding these trends will help you prepare for future opportunities and challenges.
AI advancement
Machine learning algorithms become more advanced with larger datasets and improved processing capabilities. Future systems will handle increasingly complex matching scenarios with minimal human intervention.
Natural language processing improvements enable better understanding of unstructured invoice data. AI systems will extract relevant information from emails, PDFs, and other document types that currently require manual processing.
Predictive analytics
Advanced analytics will help organizations predict and prevent invoice matching process issues before they occur. Systems will identify patterns that lead to discrepancies and recommend process improvements.
Predictive models will optimize cash flow by forecasting payment timelines and discount opportunities. This real-time visibility enables better financial planning and vendor relationship management.
Purchase order matching FAQs
Purchase order matching is the process of verifying that an invoice matches the original purchase order and receiving report before payment is approved. It ensures your organization only pays for goods or services that were ordered and received. Effective PO matching helps prevent overpayments, fraud, and errors, while improving vendor trust and payment accuracy.
Automated PO matching uses AI and machine learning to compare invoices, purchase orders, and receiving documents. These systems extract and interpret data using OCR and natural language processing, flag mismatches, and route exceptions to the appropriate team. Over time, automation improves accuracy, reduces manual effort, and speeds up invoice processing.
Manual purchase order matching is time-consuming and error-prone. Common issues include…
– Inconsistent document formats
– Price or quantity discrepancies
– Missing or partial POs
– Complex service or bundled invoices
– High volumes during peak periods
These challenges delay payments and reduce your team’s ability to capture early payment discounts or analyze spend.
– 2-way matching compares invoices with purchase orders to verify price and quantity
– 3-way matching adds a receiving report to confirm the goods or services were delivered
– 4-way matching includes an inspection report to validate quality
Each additional step increases accuracy – but also complexity – making PO matching automation more valuable.
Automation improves PO matching by reducing human error, processing large volumes quickly, and standardizing workflows. Advanced platforms like Rossum use AI to extract data across different formats, detect common discrepancies, and suggest resolution paths. This improves processing speed, reduces costs, and allows teams to focus on higher-value work.
Yes. Leading automation platforms can manage non-PO invoices such as utilities, legal fees, or marketing expenses. These invoices are tagged, coded, and routed to appropriate approval workflows. Automating both PO and non-PO invoices reduces bottlenecks at month-end and ensures accurate budget tracking across departments.
Ready to fix your AP bottlenecks?
Purchase order matching automation transforms accounts payable by eliminating manual bottlenecks, reducing errors, and freeing your team to focus on higher-value work. It delivers measurable gains in processing speed, accuracy, and cost control.
Early adopters gain the advantage, with stronger vendor relationships, better cash flow, and finance operations that scale without increasing headcount.
But the results depend on getting the foundations right – clean data, clear processes, and a phased, well-managed rollout. Manual matching may have worked in the past – but it won’t carry you forward.