How to Automate Localization Management in Accounts Payable
Processing documents from multiple countries, each with unique formats, languages, and compliance requirements is creating bottlenecks for global organizations. While many have centralized their AP functions into shared service centers, the teams still struggle with the manual burden of localization management. This post explores how automation can streamline this process to eliminate bottlenecks and reinforce your business agility.
Download your free eBook… Your AP Automation Wake-Up Call.
Calculating the Cost of Doing Nothing [2025 Edition].
Your business becomes irrelevant. Your competitors leave you standing. You’re done.
Table of Contents
- What is localization management in accounts payable?
- Examples of localization challenges
- Types of localization management approaches
- Why do businesses need automated localization management?
- How do businesses automate localization management?
- How Rossum solves localization management challenges
- Localization management best practices
- Localization management FAQs
- Ready to fix your AP bottlenecks?
What is localization management in accounts payable?
Localization management is the process of handling regional and country-specific differences in invoice formats, tax requirements, language needs, and regulatory compliance. For enterprises operating across borders, this process becomes more complex with each new market entry.
Unlike simple translation projects, comprehensive localization management involves adapting your entire accounts payable workflow to accommodate regional variations. While maintaining standardized processes and data outputs.
The challenge escalates when shared service centers try to centralize operations across regions like EMEA, North America, or APAC. These centralization efforts often clash with the intricate reality of global business operations. Straightforward on paper, the situation is exacerbated when your team must navigate…
- Invoices arriving in multiple languages and currencies
- Country-specific tax identification formats and requirements
- Varying invoice layouts and data fields
- Different e-invoicing mandates and digital signature requirements
- Local compliance regulations that frequently change
Without appropriate automation, these differences force AP teams to create manual workarounds for each country. Defeating the purpose of centralization and creating operational inefficiencies.
Examples of localization challenges
The localization challenges facing global finance teams create friction in what should be a streamlined process. Let’s look at some of the most common obstacles that hinder standardization across regions…
Language variations
A global company operating in Europe could receive invoices in German, French, Italian, Spanish, etc. Traditional OCR solutions struggle with character recognition in multiple languages, forcing manual review.
Tax format differences
VAT numbers appear in different formats across EU countries – DE123456789 in Germany vs ESA12345678 in Spain. While North American operations work with EINs and Canadian Business Numbers. Each requires validation against different rules.
Document layout variances
Invoice formats are different across countries. Japanese invoices typically place totals at the top, while European invoices usually have totals at the bottom. These layout differences confuse traditional template-based systems.
Compliance requirements
Germany asks for e-invoices to be in a standardized EN 16931 format like X-Rechnung and ZUGFeRD. Italy requires specific electronic invoice formats through SDI. France has its own e-invoicing mandates. While Mexico requires CFDI digital invoices. Each system needs different data fields and processing logic.
Take a look at How to Deliver E-invoicing Solutions with a Unified AP Platform for more details.
Currency and date formats
Whether dates appear as MM/DD/YYYY or DD/MM/YYYY can affect payment timing and accruals. Similarly, currency formatting variations – €1.234,56 vs $1,234.56 – create data validation headaches.
Types of localization management approaches
Businesses generally adopt one of three approaches to manage localization strategies. Each strategy brings compromises between local expertise and global efficiency.
1. Decentralized processing
How it works – Each country or region handles its own invoices using local staff and systems.
Advantages – Local expertise ensures compliance with regional requirements.
Disadvantages – Creates processing silos, prevents standardization, increases costs, and blocks visibility of global operations.
2. Template-based centralization
How it works – The shared service center creates a unique template for each document type from each country.
Advantages – Provides a level of standardization and centralized control.
Disadvantages – Requires hundreds or thousands of templates to be maintained. Each new vendor or format change needs manual template creation. Unable to scale efficiently.
3. Intelligent automation
How it works – AI-powered systems recognize and adapt to different document formats, languages, and regional requirements automatically.
Advantages – Eliminates template maintenance, handles new formats without configuration, scales across regions, and standardizes outputs despite input variations. Your IT team won’t need to be involved.
Disadvantages – Needs initial investment in AI technology and change management.
Why do businesses need automated localization management?
The costs of manual localization management extend way beyond the obvious inefficiencies. Understanding the impact helps quantify the ROI from automation solutions.
Financial impact
Manual localization management creates direct and indirect costs that damage your bottom line…
- Processing costs escalate – Institute of Finance & Management (IOFM) research indicates that processing an invoice manually can cost up to $16, compared to as low as $3 per invoice with automation.
- Late payment penalties stack up – When localization issues delay processing, businesses miss payment deadlines, incurring fees and damaging supplier relationships.
- Lost early payment discounts – Manual handling prevents capturing time-sensitive discounts of 1-2% that require rapid processing. For instance, a discount of “2/10 net 30” means the buyer pays 2% less if they pay the invoice within 10 days, instead of having to pay the full amount in 30 days.
Operational challenges
Beyond cost considerations, manual localization efforts create operational obstacles that limit your AP team’s effectiveness…
- Scalability limitations – Manual localization management creates bottlenecks when entering new markets.
- Resource allocation issues – Finance professionals waste valuable time on low-value tasks rather than strategic analysis.
- Error generation – Manual handling introduces errors that affect downstream systems and reporting.
Strategic disadvantages
Above all else, ineffective localization management undermines strategic finance capabilities…
- Delayed financial close – Localization challenges extend month-end closing times.
- Limited visibility – Manual processes hide global spending patterns across regions.
- Compliance risks – Human error in handling country-specific requirements creates audit vulnerabilities.
- Diminished supplier relationships – Processing delays and errors damage vendor partnerships.
How do businesses automate localization management?
Successful localization automation requires a strategic approach that combines technology with process remodeling. Implement these key components…
1. AI-Powered Document Processing
Intelligent document processing platforms use machine learning rather than rigid templates. This technological shift enables AP teams to overcome traditional localization blockers.
- Recognize and extract data from any invoice format regardless of layout
- Identify and process text in multiple languages without pre-configuration
- Adapt to new vendors and formats without manual intervention
- Validate country-specific tax IDs and compliance requirements
- Handle different date formats, currencies, and numbering conventions
These systems improve continuously, learning from each new document layout they work with.
2. Exception handling
Even with automation, some invoices will need a human to review. The difference is how these exceptions are managed. Advanced IDP technology creates a structured approach that turns exceptions into learning opportunities.
- Route exceptions to human experts based on the specific localization issue
- Provide context-aware validation suggestions
- Apply corrections across similar future documents
- Track exception patterns to identify training opportunities
The volume of exceptions requiring human review decreases with intelligent automation.
For example, while traditional template-based systems might flag 40-60% of invoices for manual review because of variable formats or data in different positions, AI systems can reduce this to 5-15% by automatically handling tasks like tax code assignments, currency conversions, and data field mapping that previously needed human intervention.
3. Output integration
Regardless of input variations, AI document processing solutions deliver consistent outputs to downstream systems. Check out the following examples of how this works in practice….
- ERP integration – A global manufacturing company could process invoices in 15 languages but deliver uniform data fields to its SAP system. This ensures a consistent chart of accounts (COA) mapping and cost center assignments across all regions.
- Financial reporting – A retail organization might combine invoice data from European suppliers – with varying tax rates and invoice formats – into regulated reporting formats for its financial management system.
- Tax compliance – An international services firm could automatically route extracted tax information from invoices in different formats to its tax software, ensuring accurate VAT handling across EU countries.
- Payment processing – A technology company might standardize payment data from invoices received in multiple currencies and formats, feeding clean data to its treasury management system. Regardless of whether the original invoice was in US dollars or European euros.
This standardization ensures downstream systems receive consistent, clean data despite the variety of incoming formats.
Learn more about how Rossum integrates with your existing systems to simplify your exception workflows.
4. Compliance updates
Remaining current with global regulations is an ongoing challenge. Automation addresses this with compliance intelligence.
- Incorporates regulatory updates without system reconfiguration
- Flags compliance issues proactively
- Maintains an audit trail of compliance checks
- Adapts to new e-invoicing mandates and digital requirements
How Rossum solves localization management challenges
At Rossum, we’ve designed our intelligent document processing platform specifically to address the unique challenges of global accounts payable operations. Our cloud-native solution powered by specialist AI agents goes beyond basic OCR to deliver localization experience and intelligence for enterprise finance teams.
Intelligent data capture
Our advanced AI engine – Rossum Aurora – is designed specifically for transactional document automation. Trained on millions of transactional documents, with outputs verified by annotators.
Unlike template-based systems that fall down when encountering new document formats, our AI combines computer vision, natural language processing, and financial domain knowledge to read documents the way your AP professionals do.
- Understands documents in 276 languages and handwriting in 30
- Improves with every document processed – adapting to your documents without specific training
- Automatically adapts to any invoice layout without needing template creation – removing IT from the picture
- Understands context to identify relevant data even when position varies
- Proprietary transactional large language model able to process structured and unstructured documents, with zero hallucinations
Document translation
Rossum’s Document Translation feature eliminates language barriers that slow down multilingual document processing.
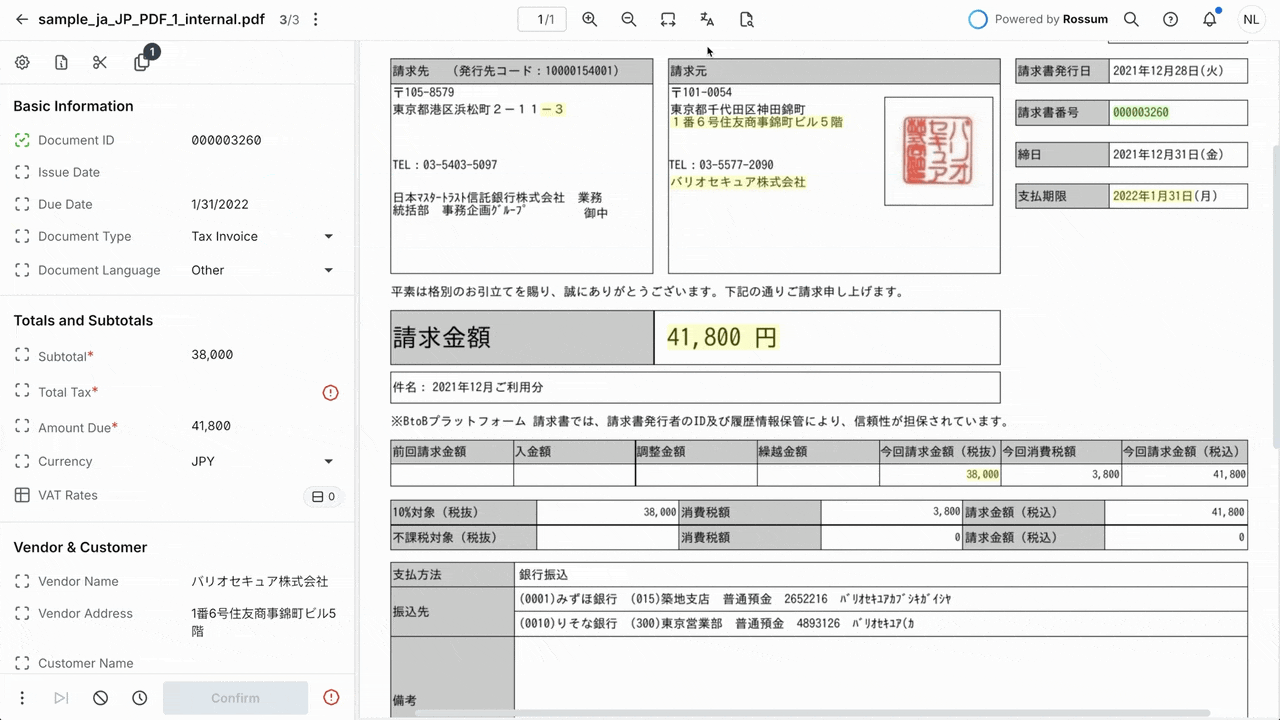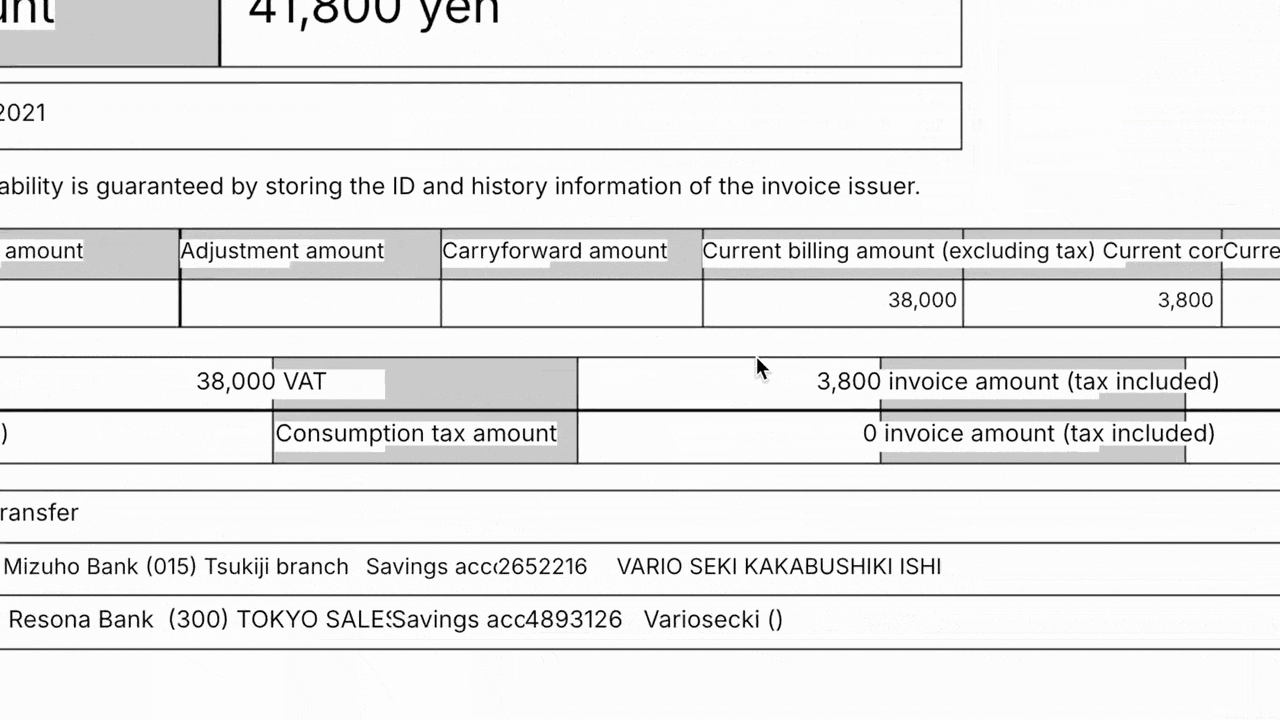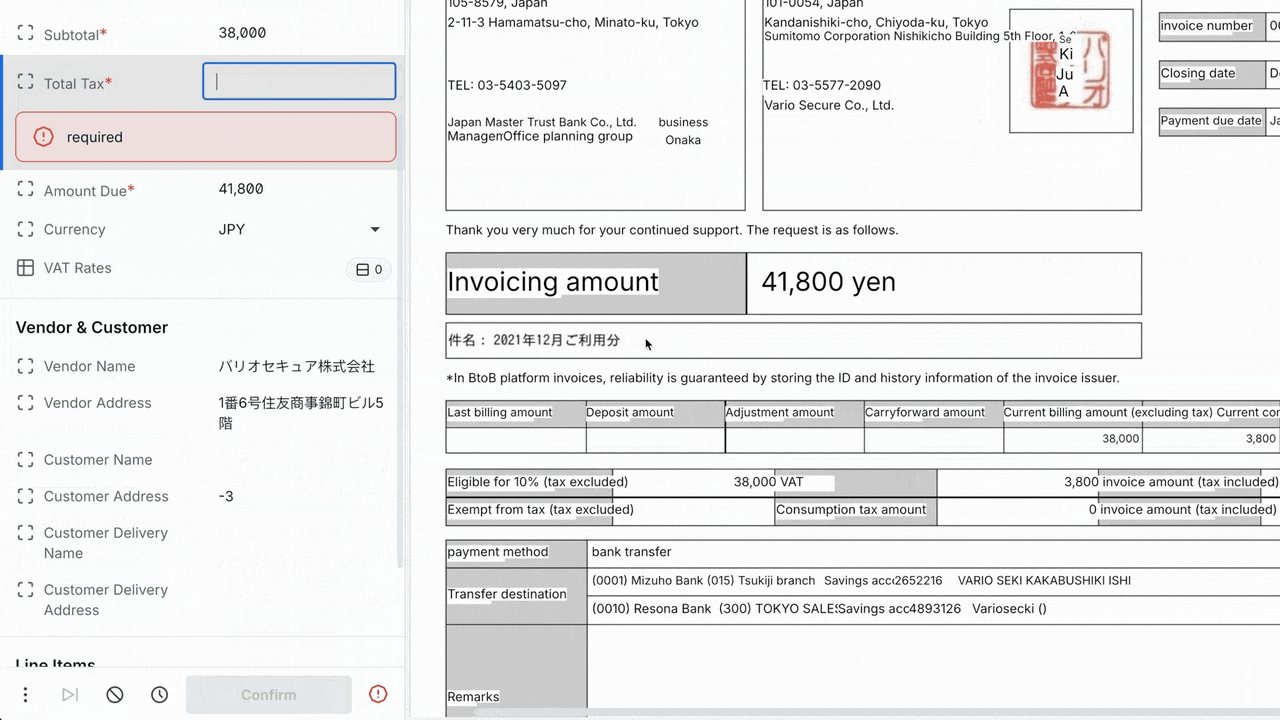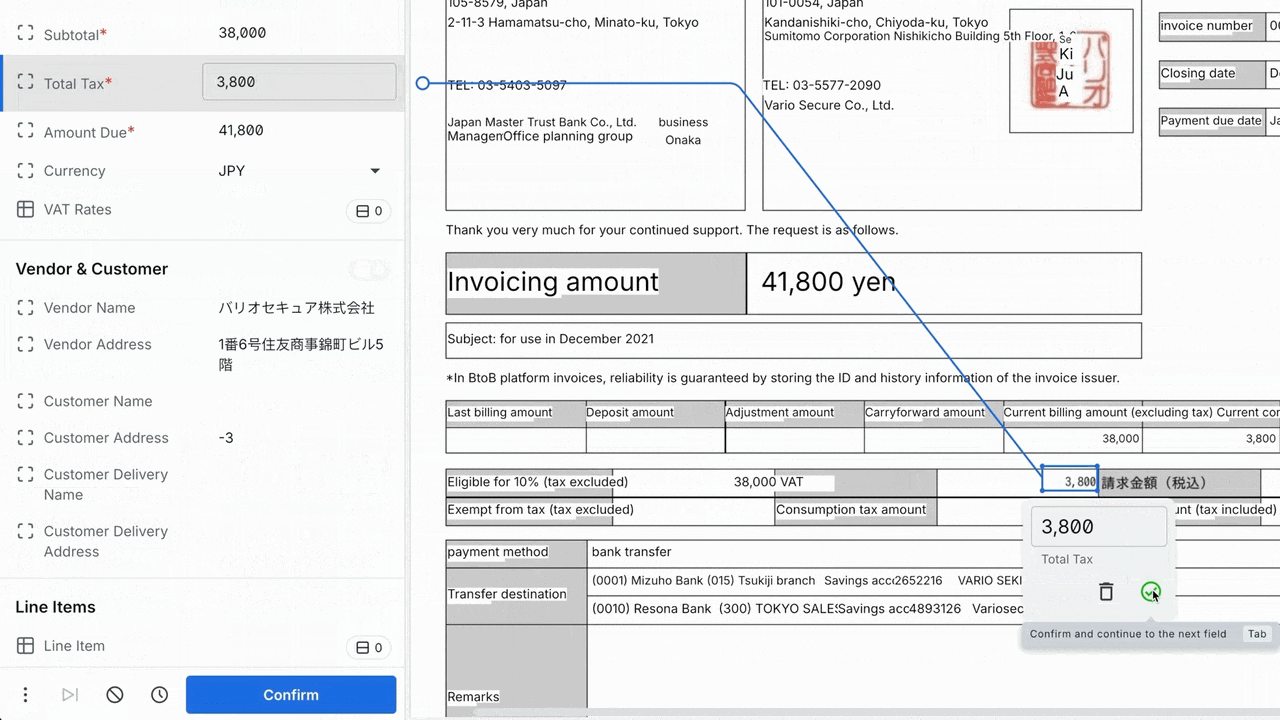
Rossum’s Document Translation feature in action.
This capability allows a single annotator to handle exceptions across all languages without external translation tools.
The feature offers one-click translation, with automatic language detection based on user profile settings.
Annotators can hover over translated values to see the original text for verification, while the system keeps the original language data and unchanged bounding boxes.
For enterprise shared service centers managing invoices, sales orders, and bills of lading in multiple languages, this feature enables…
- Streamlined exception handling across multilingual operations
- Reduced manual effort when reviewing foreign-language documents
- Improved accuracy by keeping translations within the Rossum platform
- Consistent data field training and extraction across multiple languages
This addresses the accounts payable pain point where language differences create processing bottlenecks, allowing global teams to maintain efficiency regardless of document language variety.
Proof?
“Aurora has made handling complex Japanese documents so much easier for our clients. Previously, we needed large amounts of training data, but now, Aurora’s instant learning requires minimal input and delivers fast, impressive results.
The platform’s ability to extract data from tables is particularly seamless, while providing a localized user interface in Japanese. It not only saves a huge amount of time but really empowers business users.”
Toru Fujimori, Senior Financial Engineer at MTEC
More proof?
Master Trust Bank of Japan (MTBJ), a major asset servicing bank under Mitsubishi Financial Group, was looking to improve the efficiency of processing complex financial documents.
With 40 staff manually handling thousands of sensitive papers, each taking up to 1.5 hours, MTBJ aimed to save time through automation.
They selected Rossum for its advanced AI and ability to process varied Japanese documents. Our platform trained in Japanese within days and was integrated with MTBJ’s RPA for end-to-end automation.
Now processing 100,000 documents annually, data extraction takes under 1.5 minutes and validation under a minute. Manual workload dropped by 75%, and document validation time decreased by 27.5%. Rossum is now used across 10+ departments, with future plans to support compliance and expand its use within the group.
Okay, okay, more proof…
LAPP is a global supplier of high-quality cable and connection solutions. With over 350,000 manual orders annually in EMEA, its traditional order entry process was becoming a bottleneck – slow, error-prone, and difficult to scale across a catalog of 40,000+ products.
As part of its Synergy Hub initiative in Poland, LAPP partnered with Rossum and KPMG to automate order entry. Rossum’s AI document processing solution replaced template-based OCR with a flexible, centralized solution able to handle orders in any format. Automatically extracting customer data, delivery preferences, and item details.
Localization management was key
Working with teams in Spain, Denmark, and Sweden, LAPP defined standard processes tailored to each country’s needs. Rossum’s template-free approach meant it could easily adapt to region-specific document layouts and languages, delivering a consistent experience across regions.
The result?
94.9% of order data is now captured accurately by AI. Teams have reclaimed time, cut errors, and shifted from manual entry to higher-value tasks. With just one person managing the Rossum interface, most orders flow directly into the ERP system. Boosting speed and customer satisfaction.
Localization management best practices
If you’re looking to achieve localization success, these are the best practices to accelerate your results while minimizing implementation pain points.
Kick off with data standardization
Before implementing automation, creating a strong foundation means that your system delivers consistent, usable results across all regions…
- Define consistent naming conventions for data fields across all regions
- Establish data quality standards that apply globally
- Create clear guidelines for exception handling
- Document country-specific validation requirements
Focus on comprehensive training
The effectiveness of AI systems depends on the initial training and ongoing feedback…
- Provide diverse examples from all operating regions during implementation
- Include exception cases that represent your most challenging documents
- Establish a feedback loop where corrections improve future processing
- Regularly review system performance across different countries
Implement progressive automation
A phased approach builds confidence and allows for improvement based on real-life results…
- Start with high-volume countries and document types
- Measure success with clear metrics – processing time, exception rates, cost per invoice
- Expand to additional regions based on validated results
- Progressively reduce manual intervention as confidence increases
Keep human expertise alive
Automation amplifies human capabilities rather than replacing them. Structure your team accordingly…
- Maintain country specialists who understand local requirements
- Create centers of excellence that support automation configuration
- Develop training programs that transfer knowledge across the organization
- Establish clear escalation paths for complex localization issues
Human expertise and AI automation must complement each other.
Why AI Human Collaboration is the Key to Automation’s Future is a post fueled by our Document Automation Trends 2025 report. Drilling down into why human involvement remains critical. With AI agents as digital coworkers that escalate to humans when lacking confidence or hitting guardrails.
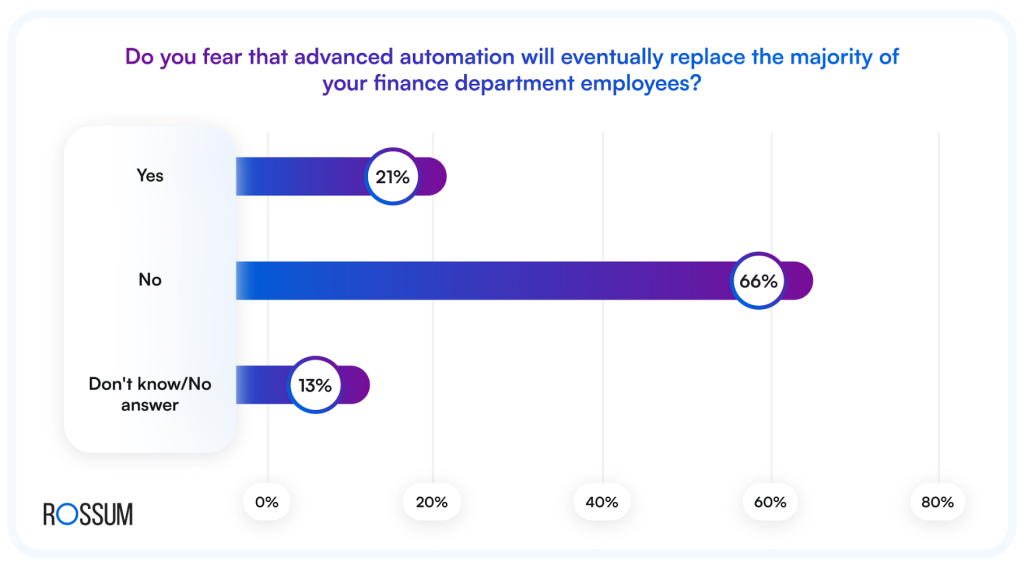
66% of finance leaders see automation as an aid, not a threat. Success will depend on balancing automation with human expertise for strategic decision making.
(2025 Automation Statistics That’ll Upset the Finance Applecart)
Localization management FAQs
Artificial intelligence solutions adapt to new formats and requirements without needing predefined templates. When entering a new target market, the system quickly learns from initial documents and applies existing knowledge about similar regions. This reduces the onboarding time for new markets compared to template-based approaches.
AI OCR software and machine learning can recognize handwritten annotations in multiple languages. While accuracy may vary with handwriting quality, the system will flag uncertain elements for human validation. The printed sections will be automatically processed.
Leading IDP solutions achieve 95-98% accuracy across common business languages and formats. Performance improves over time as the system processes more of your specific document types. Uncommon languages or highly unusual formats may initially require more validation, but accuracy increases over time.
Key metrics include reduction in processing cost per invoice, decrease in processing time across countries, fewer payment errors and duplicate payments. Increased capture of early payment discounts, reduced headcount dedicated to manual processing, and faster financial close cycles.
Intelligent document processing platforms like Rossum incorporate country-specific validation rules and can integrate with local e-invoicing networks. The software validates that incoming documents meet local requirements and flags non-compliant submissions for review.
Most companies receive both PDFs and e-invoices. A unified platform eliminates the need for separate, disconnected workflows. Rossum’s e-invoicing solution provides a single, consistent process for your AP team. Reducing complexity, lowering costs, and providing a single source of truth for all invoice data.
It’s quick and easy. Our e-invoicing solution was developed for rapid deployment, with most businesses up and running in weeks. We’ve built the platform for quick ERP integration so you can begin processing invoices without a long, complicated implementation. With predefined rules and a team of experts, you’ll be up to speed fast and ready to meet the e-invoicing compliance deadlines.
Ready to fix your AP bottlenecks?
Localization management is one of the most problematic challenges for global accounts payable operations. The manual handling of country-specific variations creates bottlenecks that sabotage the efficiency promise of shared service centers.
Implementing AI-powered document processing with built-in language capabilities and adaptive learning means enterprises can standardize their AP operations. Without giving up on compliance or accuracy.
The results impact AP operations in a positive way. Faster processing across all regions, reduced costs, improved supplier relationships, and the ability to scale globally without increasing headcount. This means your finance team can redirect their expertise from manual data manipulation to strategic financial analysis.
The successful elimination of AP bottlenecks will depend on how fast organizations implement the right solution to automate and localize their AP processes.